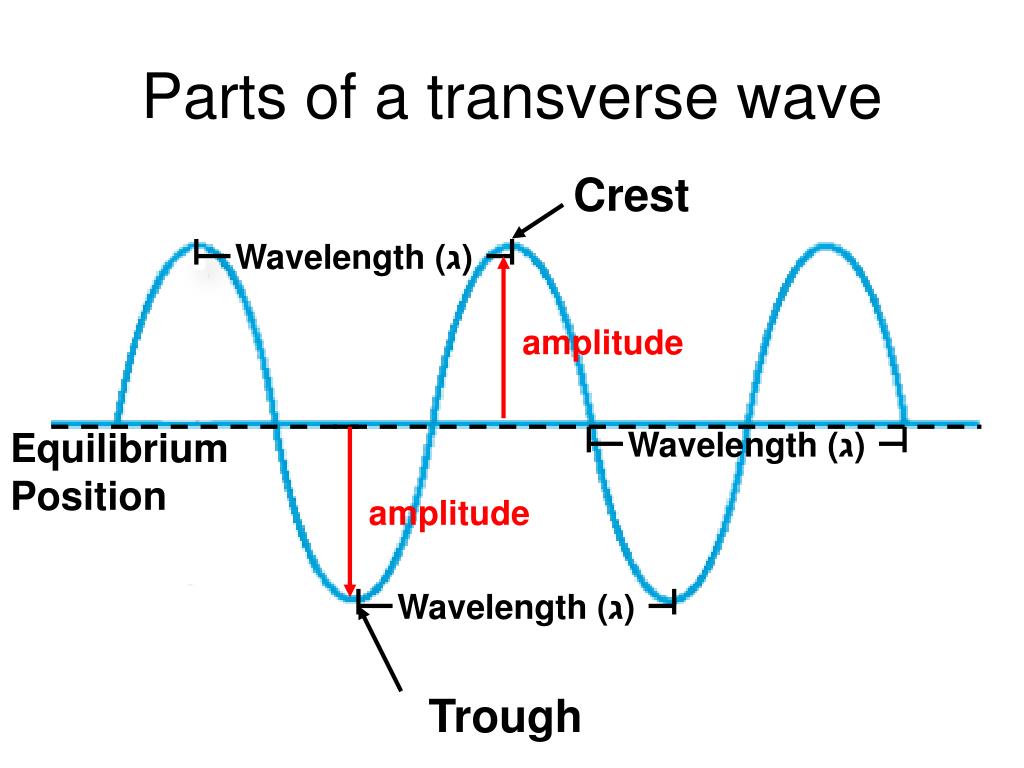
Label The Parts Of The Transverse Wave.amplitude Crest Trough Wavelength Heat exchanger spare
The speed of propagation vw is the distance the wave travels in a given time, which is one wavelength in a time of one period. In equation form, it is written as. v w = f λ. From this relationship, we see that in a medium where vw is constant, the higher the frequency, the smaller the wavelength. See Figure 13.8.

PPT Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1961289
A wave's peak is the area that's just beginning to break. It's the highest part of the wave, and the first part to break. A wave's lip is one of the most powerful parts of the wave; it's the section that begins to turn over, causing a hint of whitewater. In short, there are just a few basic wave parts. The crest, which is the highest.

Parts of a wave YouTube
What are the parts of a wave structure? A wave is described in terms of its structure. The parts of the wave include the crest, trough, period, wavelength, and amplitude. What is.
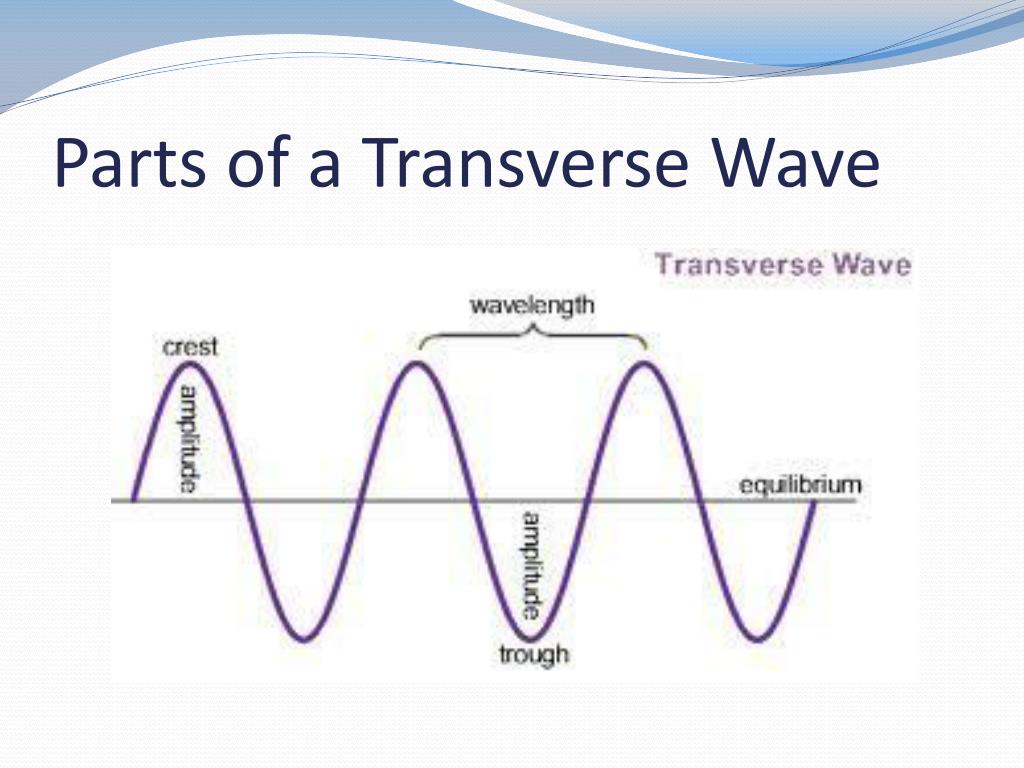
PPT Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3047701
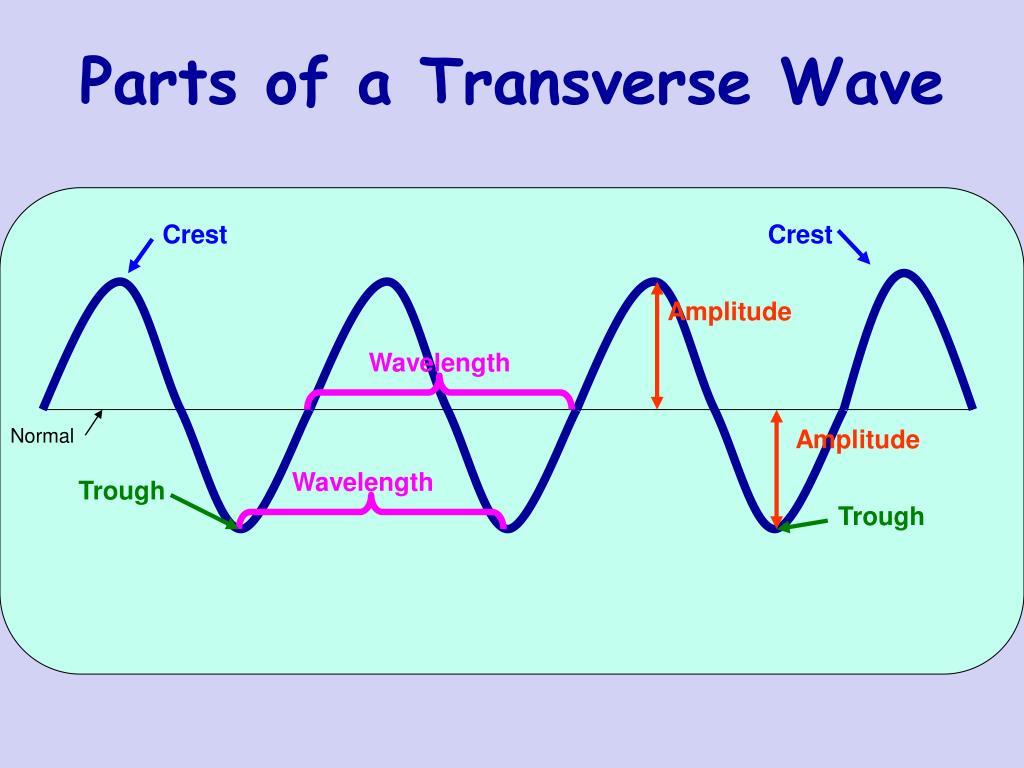
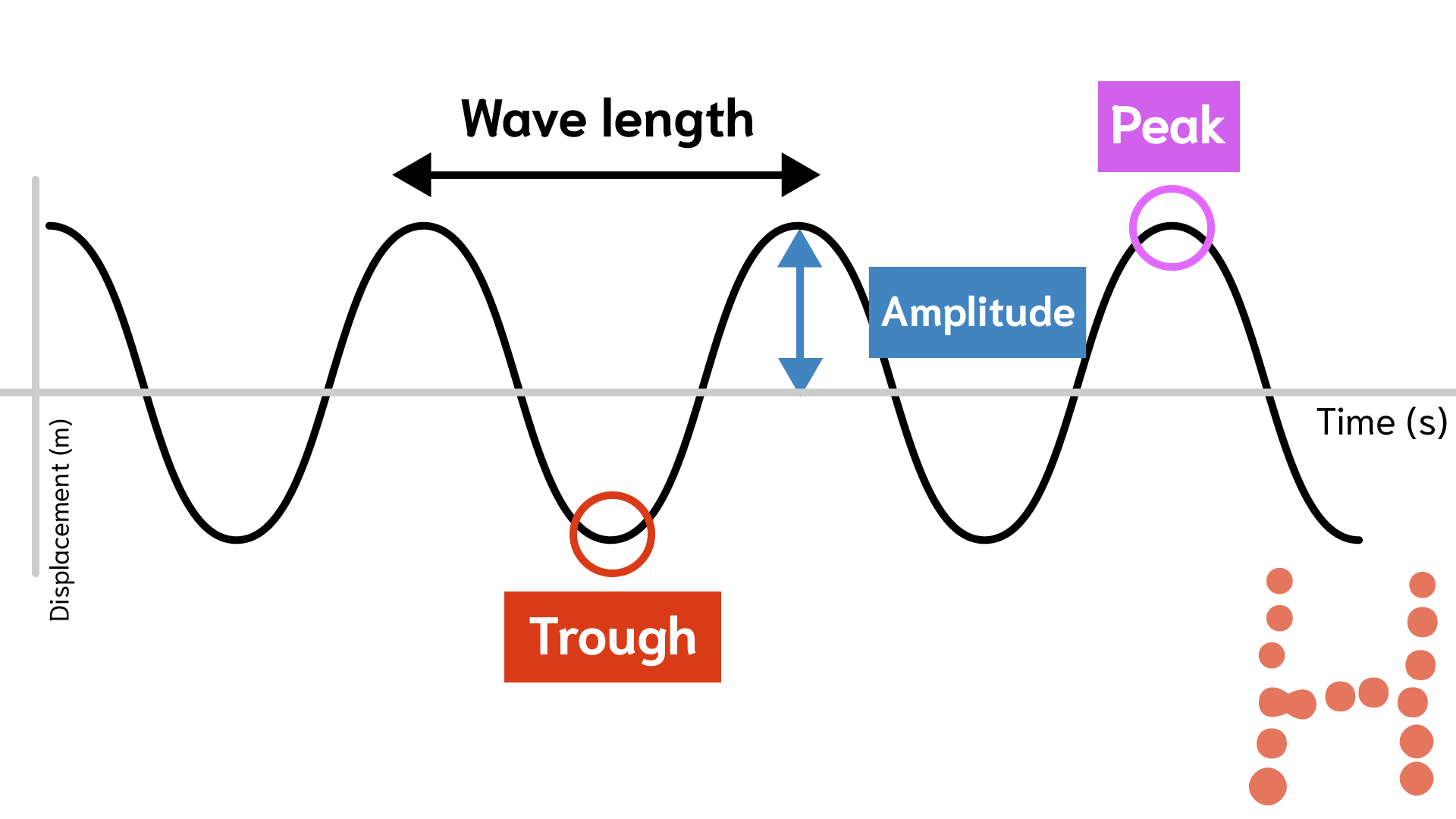
Definitions. Crest - the highest point in the wave.; Trough - the lowest point in the wave.; Wavelength - the horizontal distance between successive crests, troughs or other parts of a wave.; Wave height - the vertical distance between the crest of a wave and its neighboring trough. This term is commonly used when describing water waves where the undisturbed surface is not easily determined.

Waves Class 11 Notes, Formulas, NCERT, For NEET Leverage Edu
A traveling wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium. Consider the waves made by fans at a soccer game, as in Figure 14.1.1 14.1. 1. The fans can be thought of as the medium through which the wave propagates. The elements of the medium may oscillate about an equilibrium position (the fans move a short distance up and down), but they.
Wave Basics MooMooMath and Science
In summary, understanding the parts of a wave is crucial in unraveling the complexities of wave mechanics. By labeling the amplitude, crest, trough, and wavelength, we gain valuable insights into the nature and behavior of waves. The amplitude represents the wave's height, the crest is the highest point, the trough is the lowest.

PPT Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2197901
Students learn about the types of waves and how they change direction, as well as basic wave properties such as wavelength, frequency, amplitude and speed. During the presentation of lecture information on wave characteristics and properties, students take notes using a handout. Then they label wave parts on a worksheet diagram and draw their own waves with specified properties (crest, trough.
9 Waves and EMR Wk4 Mrs Morritt Science
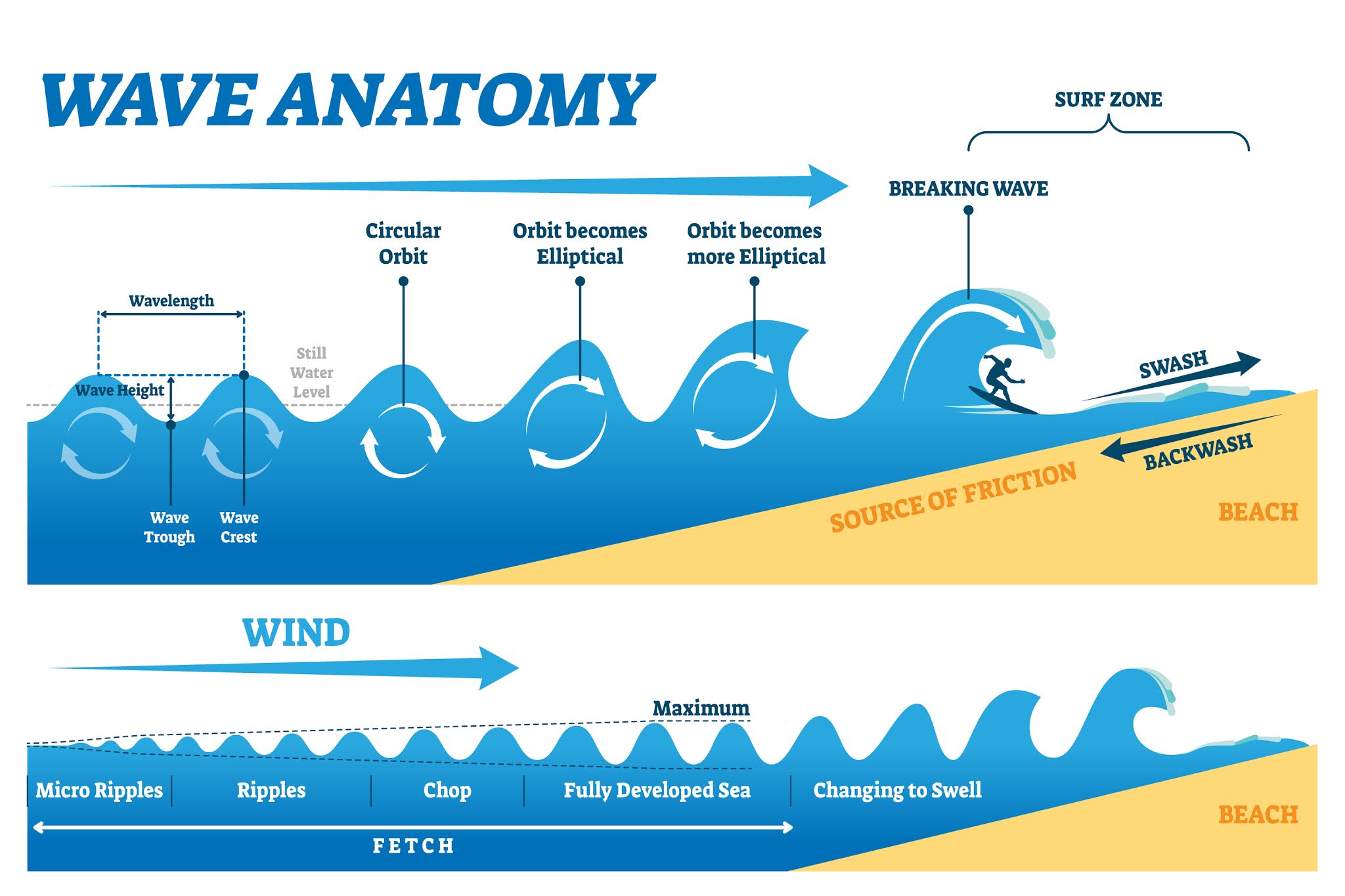
What are the parts of a wave? Photo Credits: CAVAN IMAGES All water waves have some common features, including the trough, the crest, wave height, amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. These parts are common in both deep water or ocean waves and shallow water waves. Let us get into a detailed breakdown of these parts.
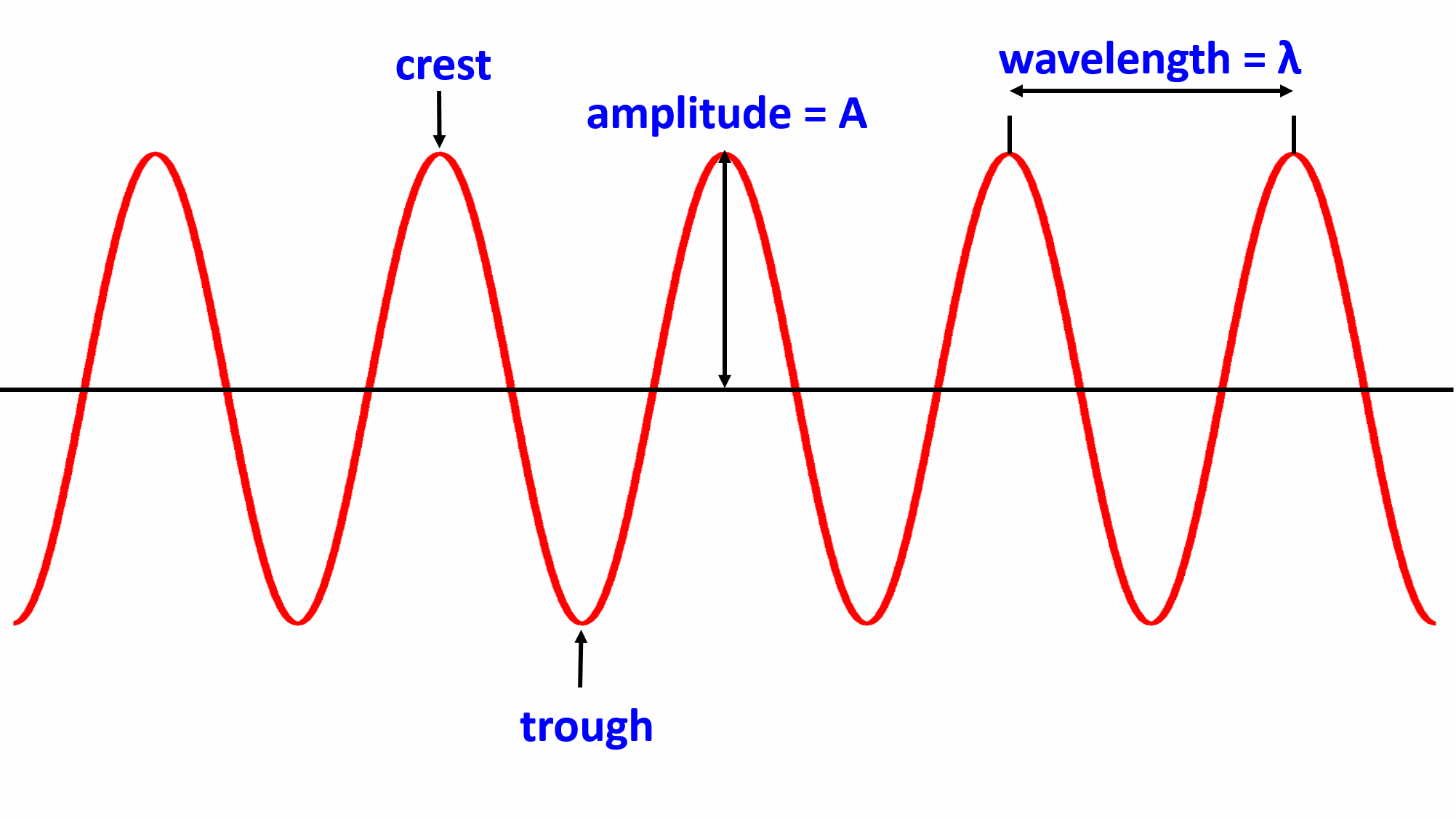
wave anatomy worksheet
Key points: A wave is a repeating disturbance that travels through matter or space transferring only energy. Below is a model of a wave. A wave's crest is its highest point, and its trough is its lowest point. A wave's amplitude is the maximum distance (positive or negative) a wave reaches from its rest position.
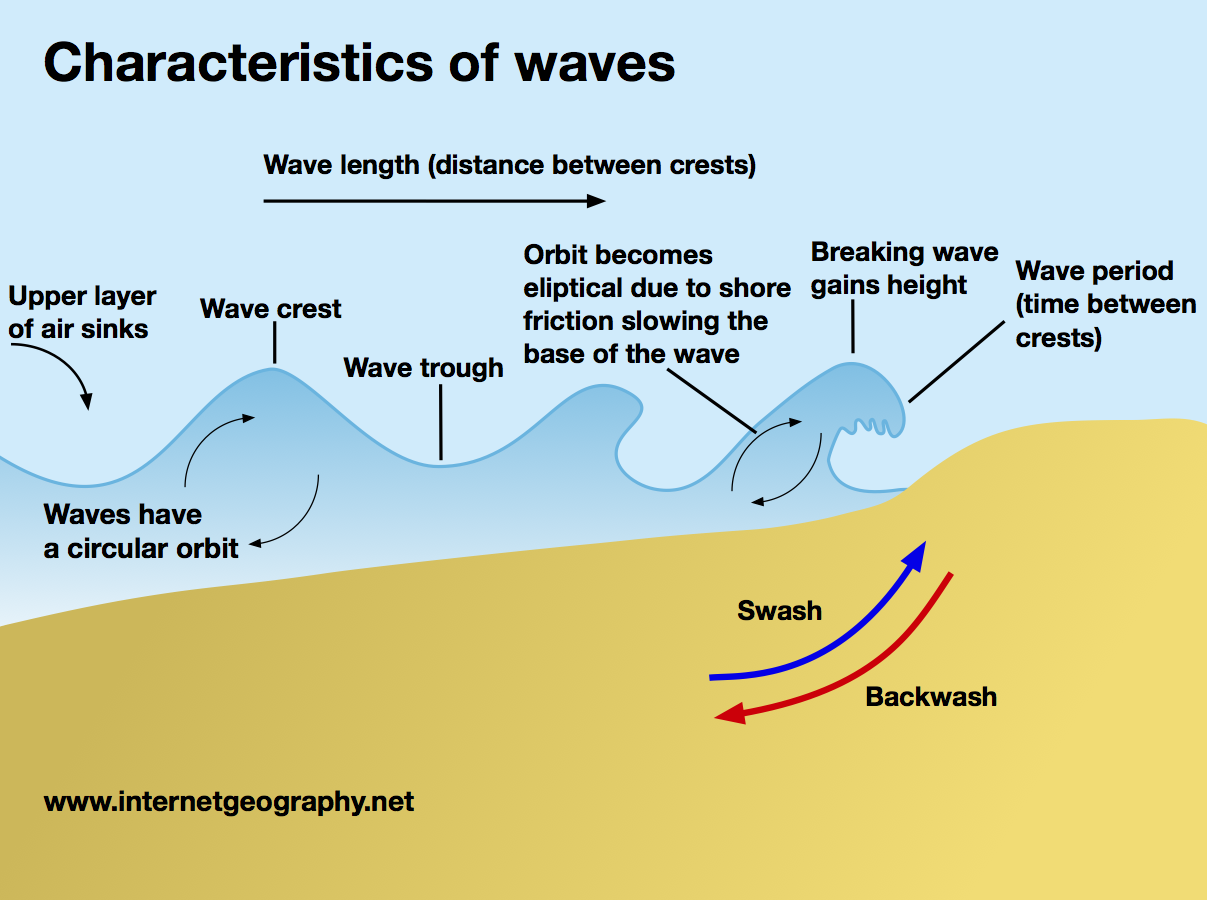
Waves A Level Geography
What are the parts of a wave? So, we've talked about what waves are. But what are the actual parts of a wave? And what types of waves are there? Some waves, such as transverse waves, have crests and troughs. The highest point on these waves is called the crest. The lowest point is called the trough.
PPT Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2998022
Types of Waves: The types of waves are given below. Transverse Waves Waves in which the medium moves at right angles to the direction of the wave. Examples of transverse waves: Water waves (ripples of gravity waves, not sound through water) Light waves S-wave earthquake waves Stringed instruments

Parts Of A Wave Diagram Hanenhuusholli
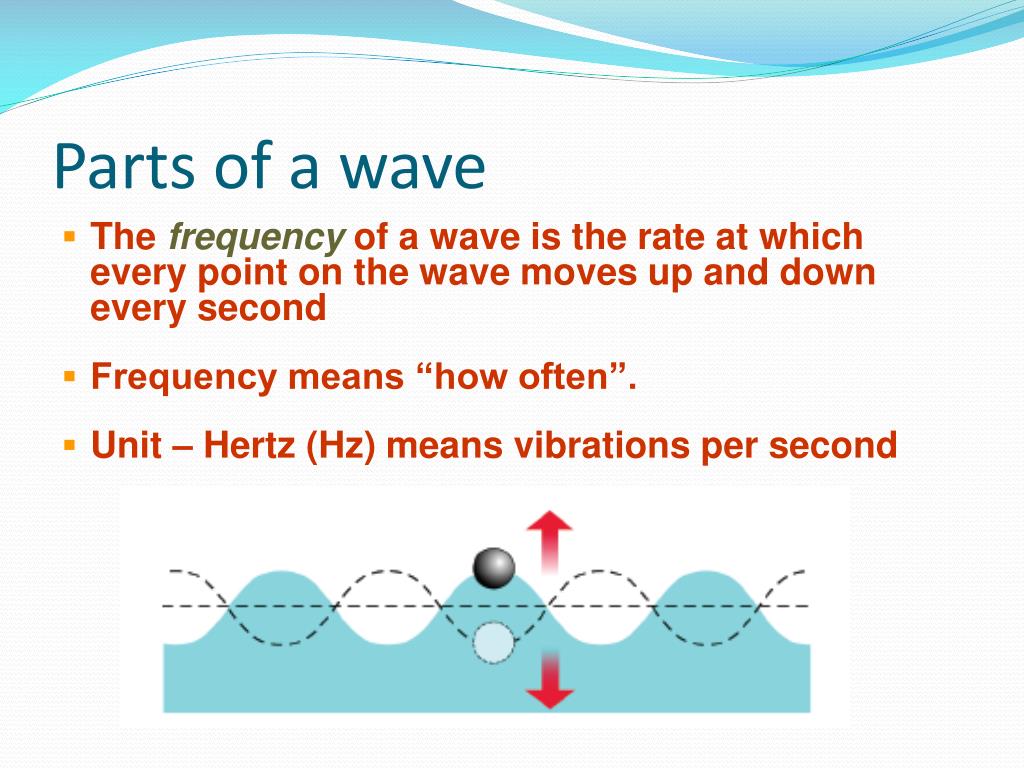
The basic properties (parts) of a wave include: frequency, amplitude, wavelength and speed. Frequency. Frequency is a measure of how many waves pass a point in a certain amount of time. The higher the frequency, the closer the waves are together and the greater the energy carried by the waves will be.

PPT CH 15 & 16 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1614788
How to identify parts of a wave Transverse waves Transverse waves vibrate the particles of a medium perpendicularly to the direction of wave travel to produce the features shown in Figure 1 below. Figure 1: Parts of a transverse wave. [What's the difference between the crest and the amplitude?] Longitudinal waves
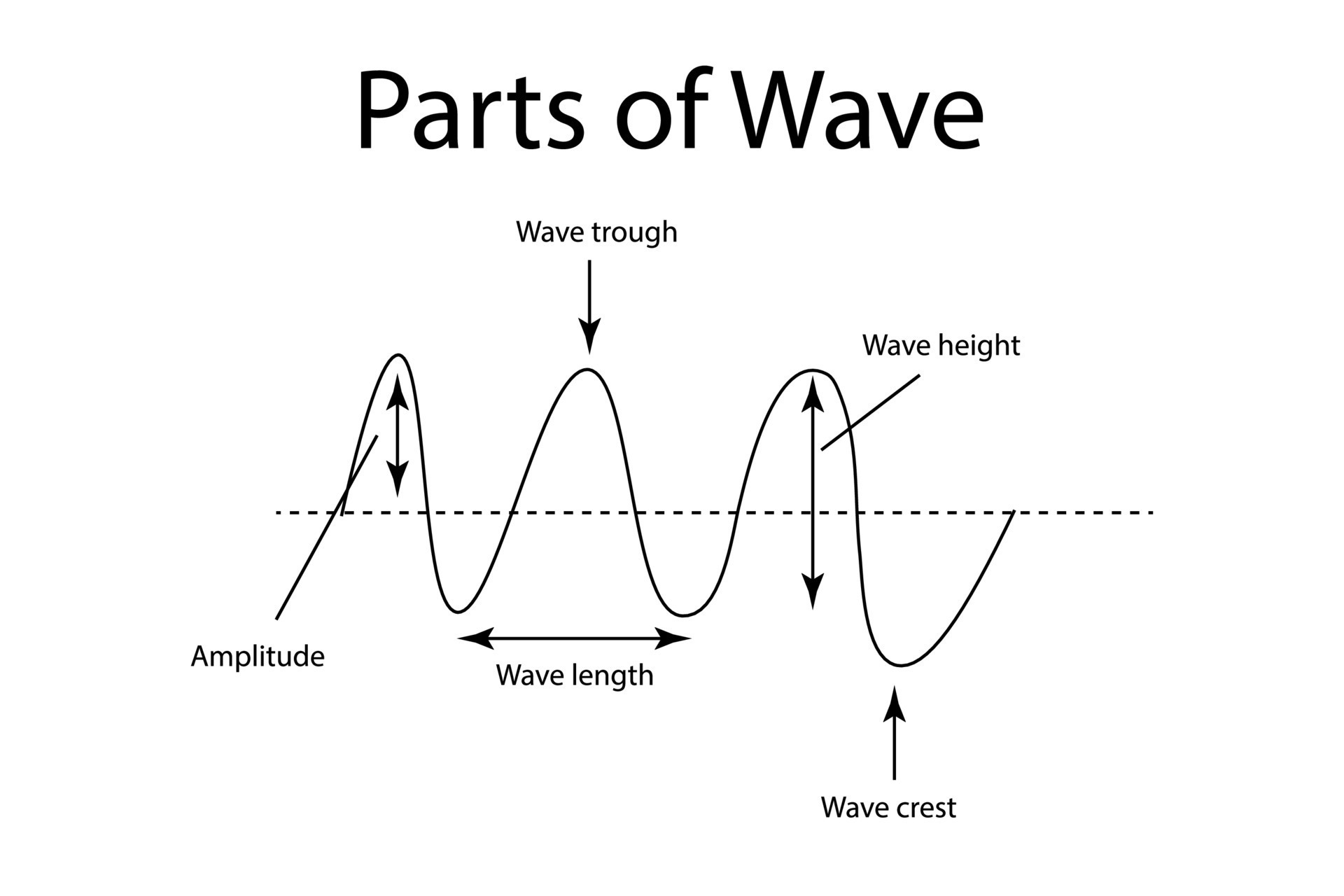
Waves of the basic properties. Vector illustration parts of a wave. Amplitude, wave length
Parts of a Wave. Lip: The lip is the top edge of the wave before it breaks. Shoulder: Is the part that is further away from the breaking part, usually not so steep. Face / Wall: The steep part of the wave out in front of where you surf. Tube / Barrel: Is the part that is hollow that surfers aim for to get a tube ride or barrel ride.
PPT Parts of a wave PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2680803
One such property is amplitude. The amplitude of a wave refers to the maximum amount of displacement of a particle on the medium from its rest position. In a sense, the amplitude is the distance from rest to crest. Similarly, the amplitude can be measured from the rest position to the trough position.
Waves Homework Help For Kids
A wave is described by its wavelength (or the distance between two sequential crests or two sequential troughs), the wave period (or the time it takes a wave to travel the wavelength), and the wave frequency (the number of wave crests that pass by a fixed location in a given amount of time).